The code discussed in this post is part of my open source anticheat and can be found here.
In the game Garry’s Mod, client and server can communicate via Netmessages. These are based on the mechanisms provided by the source engine, but can also be used via the Lua API.
If you are unfamiliar with this concept, you should first read the documentation of the Net Library and the Source Engine.
To give you a simple idea of the concept, here is a primitive example:
Server:
-- The server has to register each net message before it can be used
util.AddNetworkString("AnyIdentifierForThisMessage")
-- The server listens for the message and runs the function when it is received
net.Receive("AnyIdentifierForThisMessage", function(len, ply)
local data = net.ReadString()
print(string.format("Received data: %s", data))
end)Client:
-- The client sends the message to the server
net.Start("AnyIdentifierForThisMessage")
net.WriteString("Hello, world!")
net.SendToServer()Attack vector
Suppose we have a function on the server that is terribly optimized:
net.Receive("SuperExpensiveToCompute", function(len, ply)
-- calculate the distance between every entity
for k, v in pairs(ents.GetAll()) end
for k2, v2 in pairs(ents.GetAll()) end
local pos1 = v:GetPos()
local pos2 = v2:GetPos()
local distance = pos1:Distance(pos2)
-- ...
end
end
end)The function ents.GetAll() returns a table with all entities on the current map. On a large server, this can be over 4,000 entities. As each entity is compared with each other, this results in a complexity of \(O(n^2)\) (i.e. around 16,000,000 calculations of the distances).
In a real-time application, this can lead to serious performance problems. Developers are often unaware that attackers can inject their own Lua code into the game and send these netmessages to the server as often as they like. If an attacker finds such a function in add-ons that are used on many servers, he will have a lot of fun.
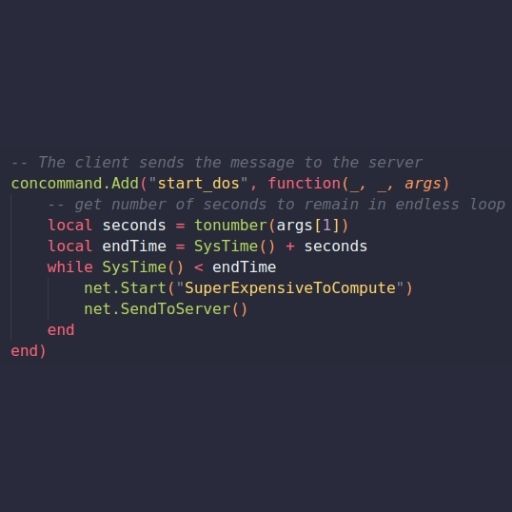
concommand.Add("start_dos", function(_, _, args)
-- get number of seconds to remain in endless loop
local seconds = tonumber(args[1])
local endTime = SysTime() + seconds
while SysTime() < endTime
net.Start("SuperExpensiveToCompute")
net.SendToServer()
end
end)Defense
One possibility would be to limit the number of netmessages per client per second to the server and ban a player that exceeds a given threshold. However, there are two problems with this:
- Poorly programmed add-ons can incorrectly send several hundred requests to the server in a very short time
- If a netmessage takes 0.2 seconds to calculate on the server side, a single-digit number of requests per second is sufficient to generate a noticeable performance impact
Instead, we calculate the time required for each net message received and add this to the respective player’s time account. The time account is reset every n seconds. If a player’s time account (e.g. 5 seconds runtime within 3 seconds) is exceeded, he will be banned from the server.
Background
The callback function defined in net.Receive is stored internally in the variable net.Receivers, where the name of the netmessage is the key:
-- see https://github.com/Facepunch/garrysmod/blob/master/garrysmod/lua/includes/extensions/net.lua#L9-L18
net.Receivers = {}
--
-- Set up a function to receive network messages
--
function net.Receive( name, func )
net.Receivers[ name:lower() ] = func
endIf the server receives a netmessage, it executes the internal Lua function net.Incoming, checks whether the netmessage exists and executes the stored callback function:
-- see https://github.com/Facepunch/garrysmod/blob/master/garrysmod/lua/includes/extensions/net.lua#L23-L40
function net.Incoming( len, client )
local i = net.ReadHeader()
local strName = util.NetworkIDToString( i )
if ( !strName ) then return end
local func = net.Receivers[ strName:lower() ]
if ( !func ) then return end
--
-- len includes the 16 bit int which told us the message name
--
len = len - 16
func( len, client )
endSolution
We overwrite the net.Incoming and calculate the runtime from the difference between the time before and after the execution of the callback function:
function net.Incoming(len, client, ...)
local header = net.ReadHeader()
local messageName = util.NetworkIDToString(header)
if not messageName then return end
-- remove header from length
len = len - 16
-- since net.Receivers only uses lowercase strings as keys
-- we transform the name to lowercase to avoid a bypass by string mismatches
messageName = messageName:lower()
local func = net.Receivers[messageName]
if not func then return end
-- calculate the time it took to process the message
local startTime = SysTime()
local _, _ = pcall(func, len, client, ...)
local endTime = SysTime()
hook.Run("networking_incoming_post", client, messageName, endTime - startTime)
endNow we save a time account for each player. After the interval time has expired, we check whether one or more players have exceeded their time account:
local processTimeCollector = {}
local nextCheck = 0
local checkInterval = 5
hook.Add("networking_incoming_post", "networking_dos", function(client, strName, deltaTime)
local steamID = client:SteamID()
-- check if the client is already in the table
if not processTimeCollector[steamID] then
processTimeCollector[steamID] = {total = 0, max = 0}
end
-- add the time to the table
processTimeCollector[steamID].total = processTimeCollector[steamID].total + deltaTime
-- check every n seconds
local curTime = CurTime()
if curTime > nextCheck then
nextCheck = curTime + checkInterval
CheckCollector()
end
end)Whether the time account has been exceeded is checked as follows:
local percentile = 0.95
local globalPercentile = 0
local sensitivities = {
["high"] = 2,
["medium"] = 4,
["low"] = 10,
}
local function IsTimeTooLong(time, steamID)
local minTime = 1
local maxTime = checkInterval * 0.9
-- Time is below minimum
if time < minTime then
return false
end
-- Time is above maximum (constant server freeze)
if time > maxTime then
return true
end
-- Check deviation from percentile
local deviation = time / globalPercentile
-- Time is below percentile
if deviation < 1 then
return false
end
local sensitity = sensitivities["medium"]
-- Time is above average
if deviation > sensitity then
return true
end
return false
end
local function CheckCollector()
local timeValues = {}
for k, v in pairs(processTimeCollector) do
-- Check if we got new data
if v.total == 0 and v.total == 0 then
continue
end
-- Check if the time is acceptable
local timeTooLong = IsTimeTooLong(v.total, k)
-- Player is not trying to cause a denial of service attack, so we can rely on that data
if not timeTooLong then
-- Insert the time into the table
table.insert(timeValues, v.max)
-- Check max time
if v.max < v.total then
v.max = v.total
end
-- Client is trying to cause a denial of service attack
else
-- ban the player
end
-- Reset time
v.total = 0
end
-- Get percentile
if #timeValues == 0 then return end
table.sort(timeValues)
local percentileIndex = math.Round(#timeValues * percentile)
globalPercentile = timeValues[percentileIndex]
end